Catedrático
Biotechnology of the Interaction of Microorganisms with Legumes and Other Plants of Agricultural Interest
Members
Research lines
- Regulation of the production of bacterial molecular signals involved in the rhizobium-legume symbiotic interaction.
- Structural determination of molecular signals involved in rhizobium-legume symbiosis (Nod factors, bacterial surface polysaccharides, flavonoids).
- Determination of the non-coding RNome of Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 and Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 and study of their role in symbiosis with their legume hosts.
- Bacterial secretion systems important in bacteria-plant and bacteria-bacteria relationships: T3SS and T6SS
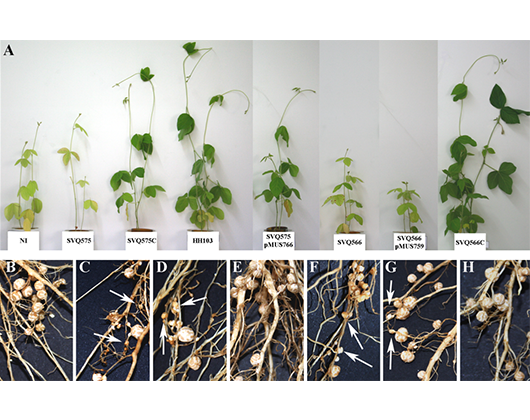
- Rhizobial effectors of T3SS involved in symbiotic compatibility with wild and improved soybean.
- Role of rhizobial membrane vesicles in symbiosis with legumes.
- Engineering of extracellular membrane vesicles of rhizobial bacteria for the development of biopesticides and plant growth promoting agents.
- Isolation and characterisation of rhizobial bacteriophages.
- Molecular mechanisms controlling the growth, colonisation or infection of phytopathogenic bacteria in crops of agricultural interest.
- Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) to study the symbiotic compatibility of S. fredii HH103 with a diverse population of wild and commercial soybeans.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence tools in protein design to increase rhizobium-legume symbiotic compatibility.
Representative publications
- Cook NM, Gobbato G, Jacott CN, Marchal C, Hsieh CY, Lam AHC, Simmonds J, del Cerro P, Navarro-Gomez P, Rodney C, Cruz-Mireles N, Uauy C, Haerty W, Lawson DM, Charpentier M. (2025). Autoactive CNGC15 enhances root endosymbiosis in legume and wheat. Nature 638, 752-759.
- Ayala-García P, Herrero-Gómez I, Jiménez-Guerrero I, Otto V, Moreno-de Castro N, Müsken M, Jänsch L, van Ham M, Vinardell JM, López-Baena FJ, Ollero FJ, Pérez-Montaño F, Borrero-de Acuña JM. (2025). Extracellular Vesicle-Driven Crosstalk between Legume Plants and Rhizobia: The Peribacteroid Space of Symbiosomes as a Protein Trafficking Interface. Journal of Proteome Research, 24(1), 94-110.
- Bernal P, Civantos C, Pacheco-Sánchez D, Quesada JM, Filloux A, Llamas MA. (2023). Transcriptional organization and regulation of the Pseudomonas putida K1 type VI secretion system gene cluster. Microbiology, 169(1), 001295.
- Fuentes-Romero F, Mercogliano M, De Chiara S, Alias-Villegas C, Navarro-Gómez P, Acosta-Jurado S, Silipo A, Medina C, Rodríguez-Carvajal MÁ, Dardanelli MS, Ruiz-Sainz JE, López-Baena FJ, Molinaro A, Vinardell JM, Di Lorenzo F. (2024). Exopolysaccharide is detrimental for the symbiotic performance of Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 mutants with a truncated lipopolysaccharide core. The Biochemical Journal, 481, 1621-1637.
- Reyes-Pérez PJ, Jiménez-Guerrero I, Sánchez-Reina A, Civantos C, Moreno-Castro N, Ollero FJ, Gandullo J, Bernal P, Pérez-Montaño F. (2025). The Type VI Secretion System of Sinorhizobium fredii USDA257 Is Required for Successful Nodulation With Glycine max cv Pekin. Microbial Biotechnology, 18(3), e70112.
- Acosta-Jurado S, Alías-Villegas C, Navarro-Gómez P, Almozara A, Rodríguez-Carvajal MA, Medina C, Vinardell JM (2020). Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 syrM inactivation affects the expression of a large number of genes, impairs nodulation with soybean, and extends the host‐range to Lotus japonicus. Environ Microbiol. 22: 1104-1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14897.
- Jiménez-Guerrero I, Acosta-Jurado S, Medina C, Ollero FJ, Alias-Villegas C, Vinardell JM, Pérez-Montaño F, López-Baena FJ. (2020). The Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 Type III secretion system effector NopC blocks nodulation with Lotus japonicus J Exp Bot. 71: 6043-6056. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa297.
- Bernal P, Furniss RCD, Fecht S, Leung RC, Spiga L, Mavridou DA, Filloux, A. (2021) A novel stabilization mechanism for the Type VI secretion system sheath. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 118:e2008500118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2008500118.
- de la Osa C, Rodríguez-Carvajal MÁ, Gandullo J, Aranda C, Megías M, Ollero FJ, López-Baena FJ, Monreal JA. (2021) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria modulate the concentration of bioactive compounds in tomato fruits. Separations 8:223. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110223.
- Alias-Villegas C, Fuentes Romero F, Cuéllar V, Navarro-Gómez P, Soto MJ, Vinardell JM, Acosta-Jurado S. (2022) Surface motility regulation of Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 by plant flavonoids and the NodD1, TtsI, NolR, and MucR1 symbiotic bacterial regulators. 2022. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147698.
- Navarro-Gómez P, Fuentes-Romero F, Pérez-Montaño F, Jiménez-Guerrero I, Alías-Villegas C, Ayala-García P, Almozara A, Medina C, Ollero FJ, Rodríguez-Carvajal MÁ, Ruiz-Sainz JE, López-Baena FJ, Vinardell JM, Acosta-Jurado S. (2023) A complex regulatory network governs the expression of symbiotic genes in Sinorhizobium fredii Front Plant Sci. 14:1322435. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1322435.
Grants
- Francisco Pérez Montaño. Mejora de la resiliencia de los cultivos a través de interacciones planta-microorganismo. Universidad de Sevilla. 2025/00000660. 01/06/2025-31/05/2026.
- Estudios de mecanismos de regulación alternativos para la síntesis de señales simbióticas en rizobios. PID2022-141156OB-I00. 01/09/2023 – 31/08/2026
- Mejorando el diálogo simbiótico a través de vesículas de membrana rizobianas. PID2021-122395OA-I00. 01/09/2022 – 31/08/2026
- Engineering extracellular membrane vesicles from rhizospheric bacteria for the development of biopesticides and plant-growth promoting agents. PROYEXCEL_00450. 02/12/2022 – 31/12/2025.
- Señalización sistémica en la simbiosis rizobio-leguminosa y nutrición nitrogenada. Efectos sobre la productividad vegetal. PID2021-122353OB-I00. 01/09/2022 – 31/08/2025
Relevant methods
| SUPPORT | METHODOLOGY |
| 1. Thermo scientific liquid chromatography system. | Determinación de factores de nodulación. |
| 2. Nanosight ns300 marvern panalitycal nanoparticle analyzer. | Aislamiento de vesículas extracelulares de membrana. |
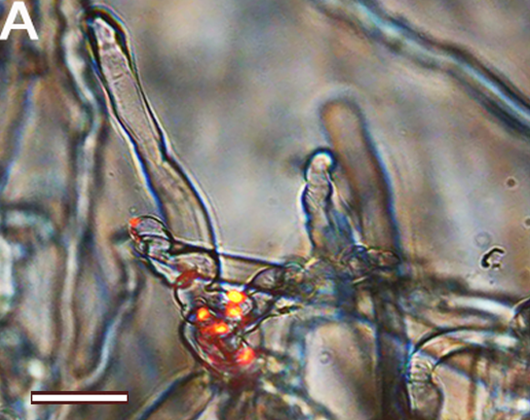
| 3. Zeiss fluorescence apotome.2 microscope. | Visualización del progreso de la infección: colonización, tubos de infección y nódulos. Localización de proteínas e interacción entre proteínas en hojas de tabaco. |
| 4. Cromatógrafo de gases. | Cuantificación de la fijación de nitrógeno por ARA (acetylene reduction assay) |
Collaborations with other national and international research groups
- David S. Guttman – University of Toronto, Canadá
- Dieter Jahn – Technischen Universität Carolo-Wilhelmina Zu Braunschweig, Alemania
- Sussane Sievers – Universität Greifswald, Alemania
- Federico Martinelli – Università Degli Studi di Firenze, Italia
- Ignacio Poblete Castro – Universidad de Santiago de Chile
- Saul Burdman – The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
- Maria Camacho Martinéz Vara Del Rey – IFAPA, España
- Alessio Mengoni – Università Degli Studi di Firenze, Italia
- José Ignacio Jiménez Zurdo – Estación Experimental del Zaidín, España
- María José Soto Misfutt – Estación Experimental del Zaidín, España
- Myriam Charpentier – John Innes Centre, Reino Unido
- Juan Sanjuan Pinilla – Estación Experimental del Zaidín, España
- Jens Stougaard – Aarhus Universitet, Dinamarca
- Flaviana Di Lorenzo – Università Degli Studi Di Napoli, Italia
- Mariangela Hungria – EMBRAPA Soja, Brasil
- Thomas Martin – Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Brasil
- Alain Filloux – Imperial College of London, Reino Unido
- Despoina Mavridou – University of Texas at Austin, EEUU
- George diCenzo – Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canadá
- Chang-Fu Tian – China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
- Zhen-Tao – Heilongjiang Academy of Sciences, Harbin, China
- Peter Kaló – Institute of Plant Biology, HUN-REN Biological Research Centre, Szeged, Hungría